What Rating Is Used To Specify The Size Of A Ups
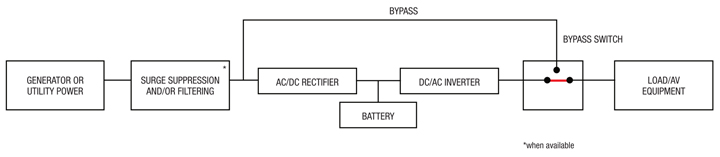
Nigh everyone has experienced a truly memorable power loss at home or at work, and the experience left them wanting more protection in the upshot of future electric interruptions. As many are starting time to see across the variety of business organisation and personal applications where sophisticated audio and video technologies are in use, a power loss tin can not only be a nuisance, but may cause permanent harm or render a whole organization inoperable. Even in cases where emergency generators are in place, there will be a short-term power loss until the generator equipment can produce 100% of the ability required past the load. Bridging this gap and providing increased defense confronting electrical calamity is a applied science formerly associated mainly with largescale data centers or applications specific to IT and networks: The Uninterruptible Ability Supply (UPS). Now that AV equipment is most purely digital and rack-mountable, just like networking equipment, the aforementioned principles and best practices can also be practical to its protection.
A UPS tin provide benefits in a variety of applications, and a deeper understanding of the factors important to selecting the right UPS would be of tremendous aid. Allow's look at different UPS features and requirements in society to improve place the right pick for your customer or application.
Place equipment to support
In order to best ascertain which components in a system are essential and therefore must receive power in the event of a ability outage and/or emergency, it'due south a good idea to take a await at the system start as a whole and so carve up it up into parts. A bit of analysis may evidence that not all equipment in an AV organisation will crave the use of a UPS, potentially saving on equipment toll and reducing the concrete weight in racks and other storage locations.
From a meridian-level standpoint, start by asking what the purpose is for the room or building organisation in question. What role does it play in the finish-user's life or livelihood? How much does present and brusk- and long-term future success depend on the operation of this system? What value is placed on the system rebooting properly, without loss of retentiveness from sudden ability cutoff?
Adjacent, zoom in on the individual components or parts of a facility-broad solution. When thinking about using UPS systems, a skilful hierarchy is to start with safety, then security, so everything else. Safety requirements are covered in detail inside a commercial building's specifications.
Large residences may also have this level of particular, merely not always. Typical safety equipment might include intercom, as well as life safety systems, and these devices may or may non be located within a rack. When considering security, devices such equally electronic door locks, airtight-excursion cameras and communication equipment (routers and switches) must exist reviewed. The final consideration is convenience, which may pertain to AV and automation systems, unless their purpose is specified as a requirement. Call up, some things should never exist backed upwards, such as equipment with electrical motors, HVAC.
Elsewhere in a facility, many control arrangement components demand to exist backed upwards due to the sensitivity of those devices and the potential loss of configuration data upon reboot. (For more information on what types of AV gear should and shouldn't exist backed upwardly by a UPS, please see the related sidebar.)
In taking this piecemeal approach to bombardment backup, several patterns will become apparent, allowing for more than efficient determination of needs on subsequent installations.
Identify maximum load
Following the determination of which pieces of equipment will crave UPS backup, it is necessary to establish the full power needs (also known equally electric current draw, or load) represented by that equipment. Several elements of quantification get into determining power requirements, and all must exist considered carefully to reduce the risk of over-technology a system and bravado a upkeep instead of a power supply.
There are two basic methods for determining the required UPS rating: Nameplate calculation and the power measurement method.
For the nameplate rating calculation method, either the VA or Watt rating must be determined for each piece of equipment that will be connected to the UPS. The fastest manner to discover the maximum load of individual pieces of equipment is to refer to the manufacturer's specifications, either every bit documented by the equipment builder in a user manual, or by checking the dorsum of hardware to wait for a power rating sticker.
Power may be rated in Watts or Volt Amperes (VA), or some combination of those quantifiers. In lodge to size a UPS, ratings for VA and Watts must both be known. In cases where the VA is not listed, just the label specifies the number of volts and amps, those numbers tin can exist multiplied together to determine VA. For case, the VA for a device specifying 120 Volts and vi Amps can exist determined past multiplying 120 by half-dozen, for a total of 720VA. For a device with a "wide range" input rating, such as 100 – 240V, the current describe shown is typically at the lowest voltage, but as an approximation it is acceptable consider the rating to be 120V.
In order to determine Watts in cases where that rating is not specified, it's possible to apply a rule of pollex that multiplies the VA by a gene of 0.6, assuming the number of Watts is 60% of the VA for whatsoever given slice of hardware. For whatever equipment that is known to employ Active
Understanding the ability factor
A VA rating is Volts x Amps (in rms), and is referred to as Apparent Power
A Watt rating is VA 10 power cistron, measured by a wattmeter, and is referred to equally True Power
Why is in that location a difference in these ratings? The departure is due to something called the Ability Factor, which is a ratio of the True Power to the Apparent Power.
There are electronic techniques that can bring the power factor to unity, called Active Ability Gene Correction.
Power factor is a dimensionless number from 0 to 1. When the True Ability and Apparent Power figures are equal, the Power Factor will be 1.0 (called Unity Power Factor). This is the optimal Power Factor. In general, unless the equipment is known to have Active Ability Factor Correction, a good conservative approximate is to presume a Power Factor of 0.half dozen.
Here are some examples of typical ability factors:
Resistive loads, like incandescent calorie-free bulbs, accept a Power Factor of 1.0
Reactive loads, similar transformers or motors, can have a Power Gene of much less than 1, typically virtually 0.five (Note: Rackmount UPS systems are not designed to provide backup ability to these types of loads)
Typical electronic equipment, including modems, wireless access points, AV gear, control systems and computers, typically have Power Factors less than 1, ranging from about 0.half-dozen to 0.nine depending on how the equipment is designed
Loftier-end servers, routers and storage systems are typically Agile Power Cistron Corrected, and will have a power gene of about 1.0

Ability Factor Correction, the Watts and VA numbers will exist the same, and therefore the VA does not demand to exist multiplied by 0.half-dozen to determine Watts. It'due south not always platonic to use nameplate adding when totaling up power requirements, considering the current draw used past manufacturers to calculate VA is typically an absolute maximum value, and is unlikely to be the electric current depict under normal use. The ability factor value of 0.6 used to find the Watt rating is also typically a worst-case value. Therefore the resulting UPS specification may be larger, and therefore heavier and more expensive than what is needed for a project.
A more precise means of determining maximum load is the ability measurement method. While more complicated than just utilizing the nameplate ratings, it can reduce instances of "over-engineered" UPS systems, and therefore exist more cost constructive. To use this method, a digital power quality analyzer, such as a Fluke 43B, is required in order to accurately measure all of the parameters needed. As an culling, a true-rms digital wattmeter can be used. This equipment can be expensive, and requires an experienced operator to utilise and prepare.
A more economic and still very specific test method is to utilise an in-line energy direction device that is capable of measuring voltage, current, power and power factor and tin can be controlled by a laptop. To perform the measurement, each slice of equipment tin be measured individually under actual conditions and their ratings can exist summed for the maximum load, or if the equipment is powered past a vertical or horizontal power distribution unit (PDU), the total VA and Watts tin can be measured that style.
Once the individual power ratings for each slice of equipment requiring UPS backup are known, these can be summed to determine the total power load. Power load totals in either VA or Watts must be known to verify the size of the UPS needed for a organisation.
UPS hardware is rated with chapters in VA and Watts, ii separate factors, neither of which can be exceeded by connected hardware. For case, a UPS may take chapters to output k VA and 750 Watts. If the fastened power load exceeds either the amount of VA or Watts handled past a UPS, the device will drop the load and fill-in will fail in the result of a transition from AC to battery fill-in.
It is non sufficient to satisfy the limits of merely one of these ratings, either VA or Watts. Both must be separately considered. To elaborate with a hypothetical scenario, if the UPS is listed at yard VA and 750 Watts, failure would result in a case where total load requiring backup is 1200 VA and 750 Watts, or alternatively in a instance where the total VA requirements are less than or a total of 1000 VA, simply Watts are exceeded with a total 900 Watts drawing from the UPS. The total load requiring backup cannot exceed thou VA or 750 Watts.
Once the load is determined for each device requiring fill-in, and those figures are added together to make up one's mind the full load in both VA and Watts, it is possible to have a expert understanding of the size of a UPS required, typically expressed in VA and Watts. Using the Full VA rating and the Full Watt rating, look for a UPS that has the aforementioned or slightly greater VA and Watt ratings to ensure that the UPS will non be overloaded – a good rule of pollex is to plan for a load no greater than fourscore% of the rating.
These factors can then be used in the next step of sizing a UPS—determining run time.
Define it
Dropping the load vs. load shedding
"Dropping the Load" applies to a state of affairs when the UPS is overloaded upon transitioning to the battery and completely shuts downward. All equipment connected to a UPS that "drops the load" loses power.
"Load Shedding" is a UPS capability to preserve run time past eliminating power to sure outlets based on thresholds like time (east.one thousand., afterwards iii minutes on battery power, shut off bank number one) or battery capacity (e.thou., at 30% battery capacity, close off sure outlets/banks). Not all UPS models feature the power (via software) to configure load shedding, only where possible, it tin can extend battery ability for use past more critical devices. For example, a DVD actor may be shut downward if the power does not come back up in five minutes, in club to ensure that a router/switch remain functional. The idea is to eliminate non-disquisitional devices from the battery backup so that other devices can remain powered during a sustained ability outage.
Calculate required run time
When determining run time for a UPS, it is important to sympathise the surround in which the equipment is installed. First, determine the minimum requirements of the client or end-user. The type of facility and its workflow volition influence the adding of how long the equipment will demand to exist up during the event of a power outage when a UPS is running purely on battery, with no line voltage connected.
Next, institute whether in that location is a backup generator in the facility. If there is a backup generator on site, find out which locations are connected to the backup generator, and how long ability volition remain out until the backup generator begins to deliver power. It's like shooting fish in a barrel to overestimate how long battery fill-in will be necessary. Remember, the object of UPS fill-in is emergency or missioncritical protection. The priority is to go along equipment powered long enough for automated or transmission shutdown or until generator power initiates, or provide fill-in for mission-critical devices such as modems and routers, and other equipment deemed essential.
Required run time is a calculation of the bodily load versus the time required for the organisation to be on backup power. Equipment with a significant power load will draw downward the UPS faster, and logically it follows that AV gear with a smaller load volition draw less power. As stated in the showtime step of this white paper, AV equipment with large power draws, such as video displays or audio amplifiers, typically exercise non require backup via UPS. In most circumstances, equipment that needs to stay online draws minimal power, and therefore run time is extended.
Once load and required run time are adamant, the data can then be applied to a UPS manufacturer's estimator or determine the all-time match using a "Load Versus Run Time" chart.
When considering the specs of a UPS, it's important to note there is a correlation betwixt VA and run time. Larger VA units will typically offer longer run time for the aforementioned loads than smaller VA units. As a result, some customers get with larger units to achieve desired run time. There is a second, meliorate choice – expanded battery packs. These batteries typically measure 1U or 2U and can exist daisy-chained to a UPS in club to increase the run time without boosted toll of increased load capacity or capabilities. There are a few manufacturers who offer this option for select products. Non all battery backups on the market will accept extended run time batteries.
Choose a topology
Knowing the load, runtime and size of the UPS needed for a project leads to the side by side choice in the option of production, which is topology. The topology of a UPS is its fundamental configuration and performance and determines how information technology interacts with incoming ability and what happens when that ability becomes unavailable. There are a number of dissimilar UPS topologies, merely for this paper we'll be discussing what are considered to be the three principal types, which are: Standby, Line Interactive and Online. Each of these different designs has its ain set up of benefits.
Standby/offline
A Standby, or Offline, UPS is characterized by its minor size, short backup run time and lack of any voltage regulation. This blazon of UPS tin too have a longer transfer time—the time it takes to switch to battery once Air-conditioning power is not present. In general, this type of UPS generates a foursquare wave output.
Line interactive
A Line Interactive UPS is typically rackmount, somewhat larger in size than standby models and is differentiated past the addition of Automatic Voltage Regulation (AVR). This feature allows for small corrections, up or down, in power without switching directly to bombardment. This is accomplished via a cadet/boost transformer and is beneficial especially in circumstances when brownouts (undervoltage events) are common. It prevents the UPS from switching over to bombardment, which can assist with longevity of the internal bombardment packs.
In addition to AVR, Line Interactive UPS products generally have a faster transfer time and could be offered in two dissimilar waveform output formats. These are Faux Sine Wave and Pure Sine Wave. Nosotros'll explain the differences and applications of these different types of moving ridge forms later in the paper.
Online/double conversion
An Online, or Double Conversion, UPS is unique in that it completely isolates output power from input power. By using two inverters, input power is converted to DC and used to charge the batteries, so converted back to Ac over again for output to devices. Because of this configuration, the UPS has no transfer time and is e'er running on battery. The output is fully regulated and is always a perfect 120V, 60Hz wave, no matter what kind of input power is present. Baloney of the output waveform is very depression, generally less than three% even at full load regardless of what is happening to the utility power.
Since this is the most circuitous blazon of UPS, the size of these units tin range from larger rackmount all the way to freestanding systems that can be several whole racks or more depending on the application. This is the near expensive blazon of UPS, however, it does provide "mission-critical" level power protection. 3 caveats with the blueprint are the increased energy consumption due to the constant charging and discharging of batteries, the decreased lifespan of batteries due to constant use and increased heat generation past the UPS.
Determine waveform type
As noted in Step 4, different topologies are associated with distinct waveforms. At that place are three different types of waveforms that a UPS can output depending on its design: Square Moving ridge, Simulated (or Modified) Sine Wave or Pure Sine Moving ridge. Each waveform type has a range of applications and advantages/disadvantages.
The three waveform types are illustrated below:
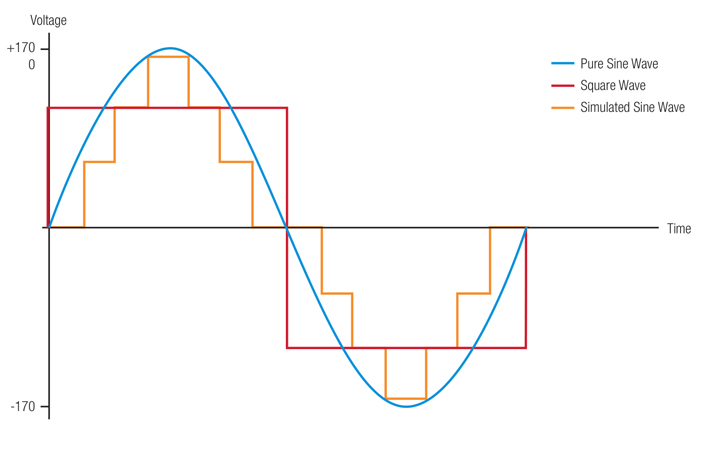
Square moving ridge output (ruby trace)
A square wave UPS is potentially the most compact in size and presents the most cost effective mode to provide fill-in ability from a battery. There are several drawbacks to this topology yet that make information technology unsuitable for AV applications. Kickoff, note that the acme of the square waveform is much lower than the sine waves. This lower peak, while still providing 120Vrms, will not fully charge up the power supply capacitors in whatever is continued to the UPS, which could event in lower headroom and less power output from audio amplifiers for instance. 2d, square waves comprise a lot of tertiary-order harmonics which can cause inductive devices, such as transformers, to overheat. Third, these high harmonics tin wreak havoc with sensitive audio circuits. For these reasons, square wave UPS topologies are not recommended for AV applications.
Simulated sine moving ridge (orange trace)
Modified/simulated (sometimes referred to as pulse width modulated), sine waves are like to a stair-step and provide a better waveform than a square wave, since they more closely stand for a true sinusoidal signal like that which is output from a typical wall outlet. As tin be seen in the graph, the peak of the imitation sine wave is about equal to the superlative of the pure sine wave, which allows the power supply filter capacitors in connected equipment to charge to their full voltage, thus ensuring optimal voltage performance. Equally load demands change, the output voltage of the UPS is regulated by increasing or decreasing the width of the peak of the fake sine (hence pulse width modulated), so this type of UPS can maintain proper output voltage nether load when it is in battery fill-in style. Most power supplies inside today's electronics can accept a simulated sine wave power signal without whatsoever effect, with the exception of devices that take agile power factor correction. Simulated sine wave UPS topologies likewise should non exist used with inductive loads (motors, transformers, etc) or sensitive audio electronics due to the high harmonic content of the waveform.

Pure sine wave (blue trace)
A pure sine wave output UPS provides a waveform that is usually amend than the waveform provided by utility companies, and is in fact what every power supply is designed to accept. It's the best possible output waveform that a UPS tin can take and it ensures that when operating on bombardment, fifty-fifty the most sensitive blazon of equipment volition operate without issue. The design of a UPS with this type of output is more complex and comes with a higher price bespeak. The very low harmonic baloney of the power makes this an excellent choice for demanding sound and video systems, and it is the simply type of output waveform that is compatible with power factor corrected power supplies.
And so how does the choice of topologies and their associated waveforms apply to AV equipment? There are several implications. If a UPS is protecting extremely expensive and sensitive equipment, information technology may be advisable to use an online/double conversion topology UPS, because information technology volition present less wear and tear on equipment and ensure that power supplies work in connected equipment power range.
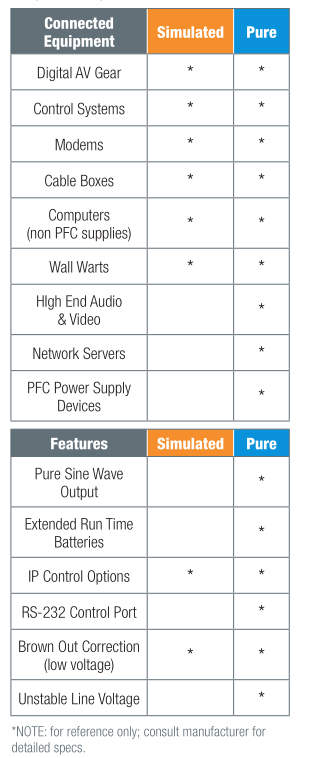
Most modern ability supplies are designed around IT equipment power supplies that can work on faux sine wave merely every bit well equally on pure sine wave. Nevertheless, to ensure that equipment will work well on fake sine wave, it is important to establish whether whatever of the attached equipment is analog or utilizes PFC (Ability Factor Corrected) power supplies. That information can exist plant as easily as by looking at the product clarification, or might exist equally hard as excavation deep into manuals to find the relevant details.
The almost mutual analog equipment in AV applications are preamps and equalizers, so pay special attention to these pieces of equipment. Not only might it be important during initial commissioning, just besides you may want to add together analog equipment in the time to come. Specifying a pure sine moving ridge UPS is an easy way to ensure the best performance. However if you lot are certain that you will non be using analog devices, and then you will be perfectly suited with simulated sine wave, which is typically only available on line interactive and double conversion battery back ups.
Based on the fact that the square waveform offers lower quality than utility power, we exercise not recommend using these models for any AV applications. Abiding under voltage during the "on battery" time will strain your equipment's power supply and might pb to premature failure. Not but that, but during the operation the power supplies will generate a lot of oestrus.
Typical Waveforms & Topologies
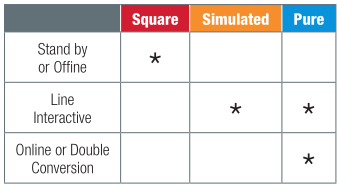
Sine wave applications
When to choose pure vs. simulated
Pure Sine Wave
- Best for audio amplifiers and analog processors, high-end video, network servers, and devices with ability cistron corrected power supplies
- Recommended for all electronic equipment
- Automatically corrects over-voltage and under-voltage conditions
Simulated Sine Wave
- Best for digital AV gear, computers (not-power cistron corrected), control systems, modems, cablevision boxes
- Automatically boosts low line voltage (brown out) conditions
Boosted UPS production requirements to consider
Number of Receptacles on the UPS Unit
Not all of the equipment in an AV system will require battery backup, or have need to be plugged into a UPS. It is of import to determine how many devices are critical and will need receptacles that are designated every bit "Battery Fill-in". Go along in mind that not all UPS models offering battery backup on all of the receptacles. Make sure to compare the exact specifications of the UPS to the number of disquisitional devices in a system to select the appropriate production.
Communication Capabilities
In some instances, there will exist a requirement for the equipment continued to the UPS to be monitored or controlled. Some UPS products enable this by including the ability to be networked connected or controlled past an Ethernet or a serial (RS-232 or USB) port. These types of products typically have individually switched or depository financial institution switched receptacles. They might too have such features such every bit incoming power monitoring and ability variable thresholds. This allows an integrator to monitor the incoming power and physically prepare the limits where the unit of measurement volition switch to bombardment. In some cases, this tin be useful when there is equipment that might be sensitive to fluctuations in voltage level.
Weight
UPS models tend to be very heavy. Whenever possible the cabinets need to exist rated for high loads and the UPS should be installed at the bottom of a chiffonier to ensure better balance and structural integrity. This is disquisitional when the installation is in an active seismic zone.
Automatic Voltage Regulation
AVR is the key feature that makes a UPS line interactive, and it corrects for small fluctuations of input voltage without having to switch to battery. This is accomplished by using a special type of transformer to either lower (buck) or raise (boost) the incoming voltage once it falls outside a predetermined range, unremarkably 120V (+/-variance dependent on manufacturer).
Appendix A
UPS run time estimation
Scenario: Abode or small business wireless internet and NAS personal deject storage protection
This system consists of three digital devices, a cablevision modem, a WiFi router and a Network Attached Storage (NAS) device with 16 Terabytes of storage. A site survey has adamant that the utility ability tin be unstable with frequent brown-outs, voltage surges and occasional service interruptions. To protect sensitive data stored on the NAS, it was adamant that a line-interactive UPS offered the best protection and would allow the user to set up the NAS to gracefully shut down in the event of a total loss of utility power. A 2nd requirement was to maintain connection to the internet for upward to 30 minutes.
Looking at the equipment nameplate ratings the post-obit was noted:
- Cable modem/router, 115-240VAC 0.5A max
- WiFi router, 100-240VAC 0.8A max
- NAS device, 19VDC up to 6.32A
And then we have a mix of data with AC current ratings and DC voltage and current, withal as we learned previously, to specify a UPS we need to know the load demand in Watts and VA. Some basic math is required. Both the cable modem and WiFi router are powered by external ability supplies, or wall warts. We volition use a line voltage of 120VAC and multiply that number past the max current draw given for each. Remember that nosotros are just multiplying volts and amperes, so the result volition be VA.
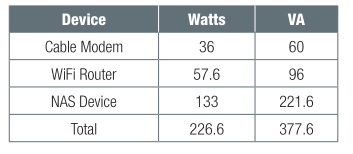
- Cable modem VA rating = 120V x 0.5A = 60VA
- WiFi router VA rating = 120V x 0.8A = 96VA
The data canvas for the NAS device simply tells usa the DC ability requirements, and then an boosted calculation is required. The ability supply for this NAS is similar to a typical laptop power "brick", and those types of ability supplies tin can have efficiencies up to 90%, meaning that only x% of the power that is consumed from the Air-conditioning line is wasted as heat. With that in heed we get-go summate the DC power to be 19VDC x half-dozen.32A which equals 120 Watts (when calculating power for DC current and voltage, the result is ever in watts, not VA). Now we know the load power, but to find the Ac power requirement nosotros need to account for efficiency so AC power = DCpower/0.nine = 120W/0.nine = 133Watts Ac power.
Since our load was calculated in watts, our AC power remains in Watts. We are left with two numbers in VA, and one in Watts but remembering that we must select a UPS based on both VA and Watts some conversions are required. The relationship between Watts and VA is dependent upon the Power Factor that each device presents to the Ac line, and a proficient rule of thumb is to use a Power Factor of 0.half-dozen.
Since Ability Factor is the ratio of Watts to VA (actual power to apparent ability) we can find whatever quantity we don't know as follows:
These are the estimated load demands in both Watts and VA. For this example nosotros are going to select a Line Interactive UPS that has automatic voltage regulation (AVR cadet and boost, to account for over-voltage and under-voltage, respectively) and a pure sine moving ridge output voltage when in battery mode.
The UPS manufacturer publishes the following run time chart for a UPS rated at 1000VA/750W (on left side).
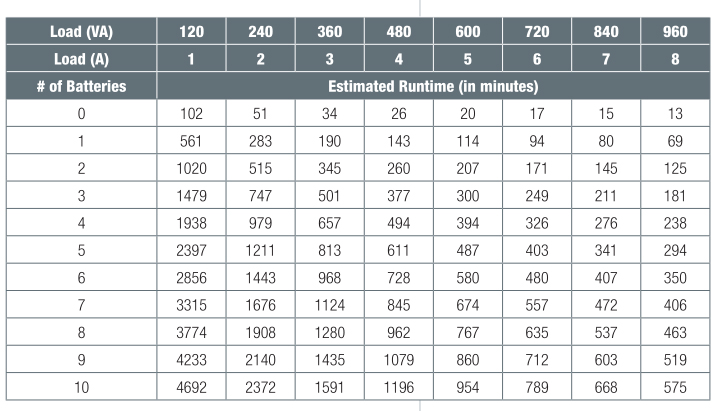
From the chart we tin can run across that with a load VA of 360 our run time would be 34 minutes, which is very shut to our requirement for a 30 minute run fourth dimension. This UPS would provide first-class protection for the NAS device and allow the system to ride out any line voltage disturbances for up to xxx minutes.
References
1. Pacific Gas and Electrical Company. Uninterruptible Power Supply http://www.pge.com/includes/docs/pdfs/mybusiness/customerservice/energystatus/powerquality/ups.pdf
2. Microchip. AN1279 Offline UPS Reference Design Using the dsPIC DSC http://ww1.microchip.com/downloads/en/AppNotes/01279A.pdf
three. EETimes. Standby and uninterruptible ability supply tutorial. http://www.eetimes.com/document.asp?doc_id=1273195
four. ON Semiconductor. Power Factor Correction (PFC) Handbook. http://www.onsemi.com/pub_link/Collateral/HBD853-D.PDF
5. Freescale. Single Phase On-Line UPS Using MC9S12E128 Designer Reference Manual. http://enshroud.freescale.com/files/microcontrollers/physician/ref_manual/DRM064.pdf?fasp=1&WT_TYPE=Reference %20Manuals&WT VENDOR=FREESCALE&WT_FILE_FORMAT=pdf&WT_ASSET=Documentation&fileExt=.pdf
half-dozen. IEEE Std 1100-1999. IEEE Recommended Exercise for Ability and Grounding Electronic Equipment. Chapter 7
What Rating Is Used To Specify The Size Of A Ups,
Source: https://hometoys.com/five-steps-to-selecting-a-ups/
Posted by: leedivening.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Rating Is Used To Specify The Size Of A Ups"
Post a Comment